Demo for state-dependent delays --- example from Humpries etal (DCDS-A 2012)
% (c) DDE-BIFTOOL v. 3.1.1(20), 11/04/2014
Humphries et al ( A. R. Humphries, O. A. DeMasi, F. M. G. Magpantay, F. Upham (2012), Dynamics of a delay differential equation with multiple state-dependent delays, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems 32(8) pp. 2701-2727 http://dx.doi.org/10.3934/dcds.2012.32.2701)
consider a scalar DDE with two state-dependent delays:

The system exhibits double Hopf bifurcations, folds of periodic orbits and torus bifurcations, which can be computed and demonstrated using DDE-Biftool.
Contents
- Add path to DDE-Biftool
- Function definitions (right-hand side and delays)
- Trivial equilibrium branch
- Periodic orbits branching off from 1st Hopf bifurcation
- One-parameter bifurcation diagram for family of periodic orbits
- Hopf bifurcation in two parameters
- Fold of periodic orbits
- Torus bifurcation continuation
- Stability of periodic orbits along torus bifurcation
Add path to DDE-Biftool
clear close all addpath('../../ddebiftool/',... '../../ddebiftool_extra_psol/',... '../../ddebiftool_utilities/');
Function definitions (right-hand side and delays)
Define the right-hand side and the state-dependent delays. We also provide their derivatives (in separate functions) to speed up execution.
Order of the parameters: p(1:2)=kappa1:2, p(3:4)=a1:2, p(5)=gamma, p(6)=c
rhs=@(x,p)-p(5)*x(1,1,:)-p(1)*x(1,2,:)-p(2)*x(1,3,:); sys_ntau=@()2; tau=@(nr,x,p)p(2+nr)+p(6)*x(1,1,:); drhs=@(x,p,nx,np,v)sys_deri_humphries_etal(rhs,x,p,nx,np,v); dtau=@(nr,x,p,nx,np)sys_dtau_humphries_etal(tau,nr,x,p,nx,np); funcs=set_funcs('sys_rhs',rhs,'sys_ntau',sys_ntau,'sys_tau',tau,... 'sys_deri',drhs,'sys_dtau',dtau,'x_vectorized',true); par_ini=[0,2.3,1.3,6,4.75,1]; indkappa1=1; indkappa2=2;
Trivial equilibrium branch
The equilibrium 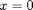 changes its stability in Hopf bifurcations
changes its stability in Hopf bifurcations
[eqbr,suc]=SetupStst(funcs,'contpar',indkappa1,'x',0,'parameter',par_ini,... 'max_bound',[indkappa1,12],'max_step',[indkappa1,0.1]); if ~suc error('equilibrium not found'); end clf eqbr=br_contn(funcs,eqbr,100); % stability [eqnunst,dom,triv_defect,eqbr.point]=... GetStability(eqbr,'funcs',funcs,'points',2:length(eqbr.point));

Periodic orbits branching off from 1st Hopf bifurcation
We continue the periodic orbits in parameter(1) (kappa1), and calculate their stability.
indhopf=find(eqnunst>0,1,'first'); [per,suc]=SetupPsol(funcs,eqbr,indhopf,'contpar',indkappa1,'degree',5,'intervals',30,... 'print_residual_info',1,'radius',1e-2); if ~suc error('initialization of periodic orbits failed'); end per.parameter.max_step=[indkappa1,0.3]; per=br_contn(funcs,per,200); disp('calculate stability') [pernunst,dom,triv_defect,per.point]=... GetStability(per,'exclude_trivial',true,'funcs',funcs); %#ok<*ASGLU> fprintf('maximum error of trivial Floquet multiplier: %g\n',max(abs(triv_defect)));
it=1, res=0.00670715 it=2, res=5.70491e-06 it=3, res=2.7812e-12 it=1, res=0.0171466 it=2, res=2.54493e-06 it=3, res=8.88453e-14 it=1, res=3.03196e-09 it=1, res=0.0462999 it=2, res=5.17741e-05 it=3, res=3.97891e-08 it=4, res=2.14688e-14 it=1, res=0.0612862 it=2, res=0.000409528 it=3, res=1.4835e-06 it=4, res=1.48815e-11 it=1, res=1.59646e-08 it=2, res=2.21728e-14 it=1, res=0.0680922 it=2, res=0.000754814 it=3, res=3.24181e-06 ...
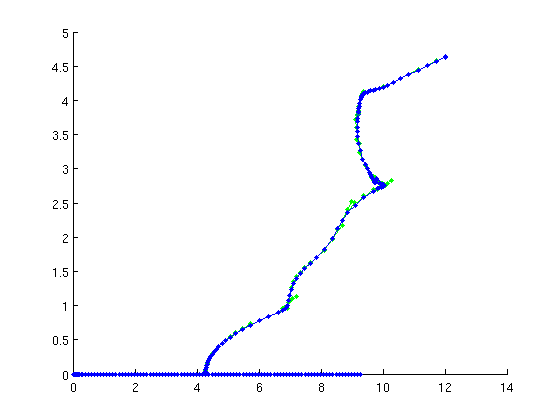
One-parameter bifurcation diagram for family of periodic orbits
Continuation parameter is 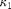 .
.
ppars=arrayfun(@(x)x.parameter(1),per.point); pmeshes=cell2mat(arrayfun(@(x)x.mesh(:),per.point,'uniformoutput',false)); pprofs=cell2mat(arrayfun(@(x)x.profile(1,:)',per.point,'uniformoutput',false)); clf clrs=colormap('lines'); pernunst_cases=unique(pernunst); amp=max(pprofs)-min(pprofs); hold on lstr={}; for i=1:length(pernunst_cases); sel=pernunst==pernunst_cases(i); plot(ppars(sel),amp(sel),'o','color',clrs(i,:)); lstr={lstr{:},sprintf('#unst=%d',pernunst_cases(i))}; %#ok<CCAT> end hold off grid on xlabel('\kappa_1'); ylabel('amplitude'); legend(lstr,'location','southeast'); grid on
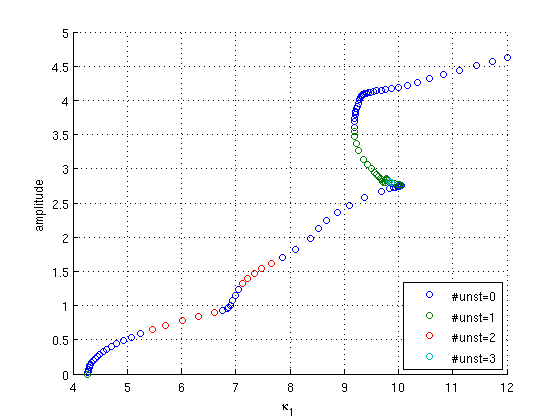
save('humphries1dbif.mat');
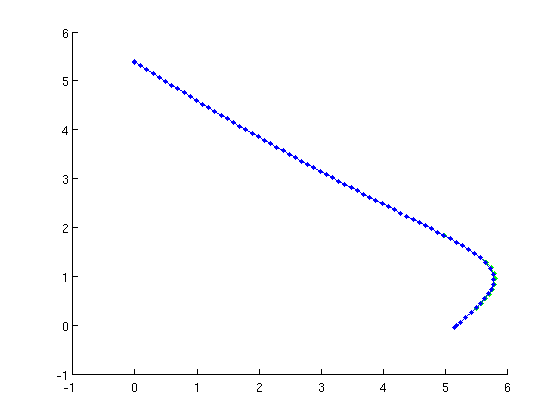
Hopf bifurcation in two parameters
Continuation parameters are 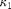 and
and  .
.
figure(2);clf [hbranch1,suc]=SetupHopf(funcs,eqbr,indhopf,... 'contpar',[indkappa1,2],'dir',indkappa1,'step',0.1,... 'max_bound',[indkappa1,12; indkappa2,10],... 'min_bound',[indkappa1,0; indkappa2,0],... 'max_step',[indkappa1,0.1; indkappa2,0.1]); if ~suc error('Hopf initialization failed'); end clf hbranch1=br_contn(funcs,hbranch1,100); hbranch1=br_rvers(hbranch1); hbranch1=br_contn(funcs,hbranch1,100); hpars=cell2mat(arrayfun(@(x)x.parameter(1:2)',hbranch1.point,'uniformoutput',false));
BR_CONTN warning: boundary hit. BR_CONTN warning: boundary hit.
Fold of periodic orbits
Continuation parameters are 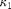 and
and  . We remove stepsize restrictions for parameters, increase the maximum number of Newton iterations. The stability along the fold may indicate codimensions. However, increasing triv_defect indicates increasing errors in Floquet multiplier computations.
. We remove stepsize restrictions for parameters, increase the maximum number of Newton iterations. The stability along the fold may indicate codimensions. However, increasing triv_defect indicates increasing errors in Floquet multiplier computations.
pf_ind0=find(diff(pernunst)==1,1,'first'); per.method.point.print_residual_info=1; per.parameter.max_step=[]; per.method.point.newton_max_iterations=8; [pfuncs,pbr,suc]=SetupPOfold(funcs,per,pf_ind0,'contpar',[indkappa1,indkappa2],... 'dir',indkappa2,'step',-0.01); if ~suc error('initialization of fold of periodic orbits failed'); end
it=1, res=3.08797 it=2, res=204.739 it=3, res=13.8964 it=4, res=0.10911 it=5, res=2.02177e-06 it=6, res=1.60907e-11 it=1, res=6.90913 it=2, res=0.109275 it=3, res=3.54579e-06 it=4, res=1.68807e-11 it=1, res=5.03447 it=2, res=2.5498 it=3, res=0.00157249 it=4, res=2.57639e-09 it=1, res=3.53685 it=2, res=0.137775 it=3, res=1.54648e-06 it=4, res=1.80291e-11
figure(2); pbr=br_contn(pfuncs,pbr,220); pbr=br_rvers(pbr); pbr=br_contn(pfuncs,pbr,60); pforbits=pfuncs.get_comp(pbr.point,'solution'); [pfstab,dom,triv_defect,pforbitstab]=GetStability(pforbits,'exclude_trivial',true,... 'locate_trivial',@(p)[1,1],'funcs',funcs); pfpars=cell2mat(arrayfun(@(x)x.parameter(1:2)',pbr.point,'uniformoutput',false)); pfmeshes=cell2mat(arrayfun(@(x)x.mesh(:),pbr.point,'uniformoutput',false)); pfprofs=cell2mat(arrayfun(@(x)x.profile(1,:)',pbr.point,'uniformoutput',false)); pf_amp=max(pfprofs)-min(pfprofs); save('humphries_pofold.mat');
it=1, res=4.67569 it=2, res=0.237738 it=3, res=8.1448e-06 it=4, res=1.57667e-11 it=1, res=8.65029 it=2, res=0.0106624 it=3, res=1.00242e-07 it=4, res=1.87544e-11 it=1, res=4.97287 it=2, res=0.0112096 it=3, res=8.28609e-09 it=1, res=15.6081 it=2, res=0.0563395 it=3, res=3.99449e-06 it=4, res=1.63558e-11 it=1, res=19.9819 it=2, res=0.0517287 it=3, res=1.94464e-06 it=4, res=1.68261e-11 it=1, res=25.2063 ...

Torus bifurcation continuation
Continuation parameters are 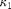 and
and  .
.
tr_ind0=find(diff(pernunst)==2,1,'first'); [trfuncs,trbr,suc]=SetupTorusBifurcation(funcs,per,tr_ind0,... 'contpar',[indkappa1,indkappa2],'dir',indkappa2,'step',-0.01); if ~suc error('initialization of torus bifurcation failed'); end
it=1, res=1.86284 it=2, res=0.117783 it=3, res=9.31292e-05 it=4, res=7.96251e-09 it=1, res=0.000106411 it=2, res=4.74679e-11 it=1, res=0.644099 it=2, res=0.0584185 it=3, res=2.90345e-05 it=4, res=2.84816e-08 it=5, res=4.46003e-11 it=1, res=8.53383e-05 it=2, res=8.48063e-11
figure(2); trbr=br_contn(trfuncs,trbr,80); trbr=br_rvers(trbr); trbr=br_contn(trfuncs,trbr,40);
it=1, res=0.168894 it=2, res=8.17217e-05 it=3, res=4.22518e-09 it=1, res=0.255921 it=2, res=0.000166909 it=3, res=1.25776e-08 it=4, res=7.84441e-13 it=1, res=0.000127848 it=2, res=6.26392e-11 it=1, res=0.391092 it=2, res=0.000343442 it=3, res=3.57833e-08 it=4, res=1.33626e-12 it=1, res=0.600864 it=2, res=0.000717279 it=3, res=9.8836e-08 it=4, res=3.52034e-12 it=1, res=0.92931 it=2, res=0.00160062 it=3, res=2.69597e-07 ...

Stability of periodic orbits along torus bifurcation
The code below demonstrates how one can use GetStability and its optional argument 'locate_trivial' to exclude the known critical Floquet multipliers from the stability consideration. Thus, the stability changes along the torus bifurcation help detect codimension-two bifurcations.
trorbits=trfuncs.get_comp(trbr.point,'solution'); trrot=trfuncs.get_comp(trbr.point,'omega'); trorbits=arrayfun(@(x,y)setfield(x,'parameter',[x.parameter,y]),trorbits,trrot); trivial_floqs=@(p)[1,exp(1i*p.parameter(end)*pi),exp(-1i*p.parameter(end)*pi)]; [trstab,dom,triv_defect,trorbitstab]=GetStability(trorbits,'exclude_trivial',true,... 'locate_trivial',trivial_floqs,'funcs',funcs);
Extract parameters, meshes and profiles of orbits at torus bifurcation
trpars=cell2mat(arrayfun(@(x)x.parameter(1:2)',trbr.point,'uniformoutput',false)); trmeshes=cell2mat(arrayfun(@(x)x.mesh(:),trbr.point,'uniformoutput',false)); trprofs=cell2mat(arrayfun(@(x)x.profile(1,:)',trbr.point,'uniformoutput',false)); tr_amp=max(trprofs)-min(trprofs); trmu=cell2mat(arrayfun(@(x)x.stability.mu(1:10),trorbitstab,'uniformoutput',false));
plot profiles of orbits at torus bifurcation
figure(3);clf plot(trmeshes,trprofs); grid on xlabel('t/T'); ylabel('x');

bifucation diagram
figure(2);clf hold on unstabsel=trstab>0; lw={'linewidth',2}; plot(trpars(1,unstabsel),trpars(2,unstabsel),'ro','markersize',4,'markerfacecolor','r',lw{:}); plot(hpars(1,:),hpars(2,:),'k-',... trpars(1,:),trpars(2,:),'r-',... pfpars(1,:),pfpars(2,:),'b-',lw{:}); set(gca,'xlim',[0,12],'ylim',[0,4]); grid on xlabel('\kappa_1'); ylabel('\kappa_2'); legend({'torus bif (unstab)','Hopf','torus bif','fold'},... 'location','southwest');

save('humphries_2dbif.mat');