Normal form calculations along Hopf bifurcation curves
Using the normal form extension nmfm by Bram Wage.
Warning Automatic bifurcation detection along branches is still in development. Its interface is likely to change, and detection is not yet reliable. With br_bifdet, normal form computations do not return error estimates. Thus, they should only be used with user-provided sys_mfderi for higher-order derivatives (in contrast to the default finite-difference approximation mf_deriv). See demo1_simple.html for an illustration, how one can perform a subset of the br_bifdet functionality with finite-difference approximations and error estimates.
(c) DDE-BIFTOOL v. 3.1.1(72), 30/12/2014
This demo requires to run demo1_hopf.html first.
Contents
- Load folder with normal form tools into matlab path
- Higher-order derivatives provided by user
- Automatic detection of codimension 2 bifurcations and criticality
- Check Criticality
- Special points
- Perform bifurcation detection along second Hopf branch
- Plot of Lyapunov coefficients for both Hopf branches
- Special points along branch3
- Save and continue with periodic orbit continuation: demo1_psol.html
%#ok<*ASGLU,*NOPTS,*NASGU> %
Load folder with normal form tools into matlab path
addpath('../../ddebiftool_extra_nmfm/');
Higher-order derivatives provided by user
Normal form calculations require higher-order derivatives. The user can (should!) provide them in the form of a function
function y=sys_mfderi(xx,par,v1,v2,...)
where y=D^m_1f(xx,p)[v1,v2,...]. The inputs xx, v1, v2 are n x (ntau+1) arrays, par the system parameters. The output is the directional derivative of order m, where m is the the number of arguments vk (k=1..m).
For this example, an explicit function for sys_mfderi is given, so we use it by adding the function to the function structure:
afuncs=set_funcs(funcs,'sys_mfderi',@sys_mfderi)
afuncs =
sys_rhs: [function_handle]
sys_ntau: @()0
sys_tau: @()[5,6,7]
sys_cond: @dummy_cond
sys_deri: @neuron_sys_deri
sys_dtau: @(it,x,p,nx,np)df_derit(funcs,it,x,p,nx,np)
sys_mfderi: @sys_mfderi
x_vectorized: 0
tp_del: 0
sys_deri_provided: 1
sys_dtau_provided: 0
sys_mfderi_provided: 1
Automatic detection of codimension 2 bifurcations and criticality
The nmfm extension provides br_bifdet, which determines Lyapunov cofficients, and codimension-two points along Hopf bifurcation curves.
The output branch_nmfm has a point array of structures that contain additional fields 'nmfm', 'nvec', 'flag'. The field 'flag' may have the values
- '' (empty): this point is not special,
- 'hoho': this point is a double-Hopf point,
- 'zeho': this point is a zero-Hopf point,
- 'genh': this point is a generalized (degenerate/Bautin) Hopf point.
The field 'nmfm' is a structure. If the branch was a Hopf curve, it contains the field
- 'L1': the first (3rd-order) Lyapunov coefficient at the Hopf point (L1<0 implies that the Hopf bifurcation is supercritical, L1>0 implies that the Hopf bifuration is subcritical).
- for special points it contains other normal form coefficients, determining the sub-case of the bifurcation. See Kuznetsov (2004) 'Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory') for notation and definitions.
branch2_nmfm=br_bifdet(afuncs,branch2);
BR_BIFDET: hoho point found at par(4) = 0.2072962661, par(7) = 8.6340742204. BR_BIFDET: omega1 = 0.3287154066, omega2 = 0.9157115877, par(4) = 0.2072962661, par(7) = 8.6340742204. BR_BIFDET: Unable to correct as hoho point near par(4) = 0.1234. BR_BIFDET: hoho point found at par(4) = 0.0000000000, par(7) = 2.4183994947. BR_BIFDET: omega1 = 0.8660253477, omega2 = 0.8660253477, par(4) = 0.0000000000, par(7) = 2.4183994947.
Check Criticality
The Lyapunov coefficients are always negative along the branch, implying that the bifurcation is supercritical.
L1_br2=arrayfun(@(x)x.nmfm.L1,branch2_nmfm.point); taus_br2=arrayfun(@(x)x.parameter(ind_taus),branch2_nmfm.point); a21_br2=arrayfun(@(x)x.parameter(ind_a21),branch2_nmfm.point); figure(17); subplot(2,1,1); plot(taus_br2,a21_br2,'.-'); grid on xlabel('\tau_s'); ylabel('a_{21}'); title('(Repeated) two-parameter Hopf curve branch2'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(taus_br2,L1_br2,'.-'); set(gca,'ylim',[-1,0]); grid on xlabel('\tau_s'); ylabel('L1'); title('First Lyapunov coefficient along branch2');

Special points
The detection routine br_bifdet finds special points, listed by br_getflags. Each row index corresponds to a type of point. Indices can be converted to point types (strings) with num2bif.
The call to br_getflags shows that br_bifdet has found two Hopf-Hopf points. Double-checking the data in the 'nmfm' field shows that one of them is genuine, the other is spurious (a non-semisimple Hopf eigenvalue when a21=0). A typical feature of DDEs is that apparently higher-codimension degeneracies can occur due to the finite number of delays and equations.
The points at which the Lyapunov coefficient L1 becomes singular (infinity) are special points: one of them is the non-semisimple Hopf eigenvalue point, the other is the Takens-Bogdanov point (where the Hopf frequency omega passes through 0). At the moment br_bifdet cannot detect Takens-Bogdanov points safely.
special_br2_alltypes=br_getflags(branch2_nmfm) knowntypes=num2bif(); biftype=num2bif(find(any(br_getflags(branch2_nmfm)>0,2))) special_br2=special_br2_alltypes(bif2num(biftype),:) for i=1:length(special_br2); fprintf('\nPoint %d normal form parameters:\n',special_br2(i)); disp(branch2_nmfm.point(special_br2(i)).nmfm); fprintf('\nPoint %d Eigenvalues:\n',special_br2(i)); disp(branch2_nmfm.point(special_br2(i)).stability.l0); end
special_br2_alltypes =
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
4 19
known point types:
type 0: stst
type 1: hopf
type 2: fold
type 3: psol
type 4: hcli
type 5: genh
type 6: hoho
type 7: zeho
biftype =
hoho
special_br2 =
4 19
Point 4 normal form parameters:
L1: -0.0127
g2100: -0.0042 - 0.0013i
g1011: -0.0091 - 0.0029i
g1110: -0.0158 + 0.0053i
g0021: -0.0086 + 0.0029i
theta: 1.0605
delta: 3.7719
Point 4 Eigenvalues:
0.1284 - 0.2509i
0.1284 + 0.2509i
0.0000 - 0.9157i
0.0000 + 0.9157i
-0.0000 - 0.3287i
-0.0000 + 0.3287i
-0.0298 - 1.0012i
-0.0298 + 1.0012i
-0.0662 - 1.6968i
-0.0662 + 1.6968i
-0.0671 - 1.6371i
-0.0671 + 1.6371i
-0.0982 - 2.4063i
-0.0982 + 2.4063i
-0.1095 - 2.3640i
-0.1095 + 2.3640i
Point 19 normal form parameters:
L1: -2.1110e+05
g2100: -1.8281e+05 - 5.4250e+04i
g1011: -3.6563e+05 - 1.0850e+05i
g1110: -3.6563e+05 - 1.0850e+05i
g0021: -1.8281e+05 - 5.4250e+04i
theta: 2.0000
delta: 2
Point 19 Eigenvalues:
0.0000 - 0.8660i
0.0000 + 0.8660i
0.0000 - 0.8660i
0.0000 + 0.8660i
Perform bifurcation detection along second Hopf branch
Along branch3 we perform normal form computations and codimension-2 detection, too.
branch3_nmfm=br_bifdet(afuncs,branch3);
BR_BIFDET: hoho point found at par(4) = 0.0000000000, par(7) = 9.6735990351. BR_BIFDET: omega1 = 0.8660252363, omega2 = 0.8660252363, par(4) = 0.0000000000, par(7) = 9.6735990351. BR_BIFDET: Unable to correct as hoho point near par(4) = 0.1065. BR_BIFDET: hoho point found at par(4) = 0.2072962626, par(7) = 8.6340742187. BR_BIFDET: omega1 = 0.9157115883, omega2 = 0.3287154065, par(4) = 0.2072962626, par(7) = 8.6340742187.
Plot of Lyapunov coefficients for both Hopf branches
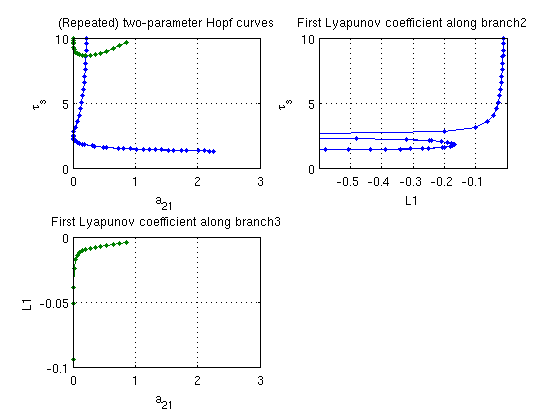
Again, at a21=0 we have a non-semisimple Hopf eigenvalue such that the Lyapunov coefficient tends to infinity. Otherwise, the Lyapunov coefficient is negative such that the Hopf bifurcation is supercritical.
L1_br3=arrayfun(@(x)x.nmfm.L1,branch3_nmfm.point); a21_br3=arrayfun(@(x)x.parameter(ind_a21),branch3_nmfm.point); taus_br3=arrayfun(@(x)x.parameter(ind_taus),branch3_nmfm.point); figure(18); subplot(2,2,1); plot(a21_br2,taus_br2,'.-',a21_br3,taus_br3,'.-'); a21lim=get(gca,'xlim'); tauslim=get(gca,'ylim'); grid on xlabel('a_{21}'); ylabel('\tau_s'); title('(Repeated) two-parameter Hopf curves'); subplot(2,2,2); plot(L1_br2,taus_br2,'.-'); set(gca,'ylim',tauslim,'xlim',[-0.6,0]); grid on ylabel('\tau_s'); xlabel('L1'); title('First Lyapunov coefficient along branch2'); subplot(2,2,3); plot(a21_br3,L1_br3,'.-','color',[0,0.5,0]); set(gca,'ylim',[-0.1,0],'xlim',a21lim); grid on xlabel('a_{21}'); ylabel('L1'); title('First Lyapunov coefficient along branch3');
Special points along branch3
Only the Hopf-Hopf point already known from branch2 and the spurious Hopf-Hopf point at a21=0 are detected as codimension-2 points.
special_br3_alltypes=br_getflags(branch3_nmfm) biftype=num2bif(find(any(br_getflags(branch3_nmfm)>0,2))) special_br3=special_br3_alltypes(bif2num(biftype),:) for i=1:length(special_br3) fprintf('\nPoint %d normal form parameters:\n',special_br3(i)); disp(branch3_nmfm.point(special_br3(i)).nmfm); fprintf('\nPoint %d Eigenvalues:\n',special_br3(i)); disp(branch3_nmfm.point(special_br3(i)).stability.l0); end
special_br3_alltypes =
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
3 12
biftype =
hoho
special_br3 =
3 12
Point 3 normal form parameters:
L1: -6.5295e+03
g2100: -5.6547e+03 - 4.8135e+02i
g1011: -1.1309e+04 - 9.6271e+02i
g1110: -1.1309e+04 - 9.6271e+02i
g0021: -5.6547e+03 - 4.8135e+02i
theta: 2.0000
delta: 2.0000
Point 3 Eigenvalues:
0.0501 - 0.2766i
0.0501 + 0.2766i
0.0501 - 0.2766i
0.0501 + 0.2766i
0.0000 - 0.8660i
0.0000 + 0.8660i
0.0000 - 0.8660i
0.0000 + 0.8660i
-0.0459 - 1.4920i
-0.0459 + 1.4920i
-0.0459 - 1.4920i
-0.0459 + 1.4920i
-0.0801 - 2.1310i
-0.0801 + 2.1310i
-0.0801 - 2.1310i
-0.0801 + 2.1310i
Point 12 normal form parameters:
L1: -0.0094
g2100: -0.0086 + 0.0029i
g1011: -0.0158 + 0.0053i
g1110: -0.0091 - 0.0029i
g0021: -0.0042 - 0.0013i
theta: 3.7719
delta: 1.0605
Point 12 Eigenvalues:
0.1284 - 0.2509i
0.1284 + 0.2509i
0.0000 - 0.9157i
0.0000 + 0.9157i
0.0000 - 0.3287i
0.0000 + 0.3287i
-0.0298 - 1.0012i
-0.0298 + 1.0012i
-0.0662 - 1.6968i
-0.0662 + 1.6968i
-0.0671 - 1.6371i
-0.0671 + 1.6371i
-0.0982 - 2.4063i
-0.0982 + 2.4063i
-0.1095 - 2.3640i
-0.1095 + 2.3640i
Save and continue with periodic orbit continuation: demo1_psol.html
See also demo1_simple.html for an illustration, how to use ddebiftool_utilities to perform a subset of the above computations without user-provided derivatives.
save('demo1_normalforms_results.mat');